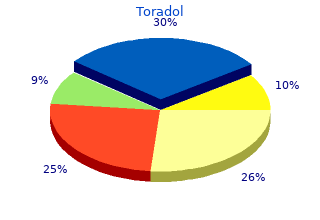
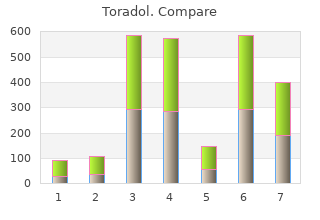
Toradol
2018, Lees-McRae College, Karrypto's review: "Toradol 10 mg. Only $0,34 per pill. Effective online Toradol OTC.".
The shaft is moved to a more lateral and distal posi- A lengthening of around 1–1 buy discount toradol 10mg intractable pain treatment laws and regulations. The surgeon must be very teric fragment is moved distally; a preoperatively purchase toradol 10mg on line pain relief medication for uti, b postoperatively careful, however, to avoid injury to the vessels that enter a b c d ⊡ Fig. X-ray series for a 12-year old boy after a congenital hip teric elevation. A femoral neck lengthening osteotomy was imple- dislocation and lateral femoral head necrosis with lateral epiphyseal mented to correct the length of the femoral neck and the lever arm of closure, head-in-neck position and shortening of the femoral neck (a). Situation 1 year postoperatively (d) At 14 years of age on completion of growth (b) pronounced trochan- 193 3 3. The acetabulum is pulled ventrally and pressure in the joint is increased as a result of lengthening laterally. A triangular wedge of bone secures the result- of the femoral neck, the procedure is indicated only if the ing position. The pivot point for the transfer is the sym- joint conditions are good (largely normal). This operation flattens an excessively steep ac- etabular roof, improves the roof coverage ventrally and Pelvic procedures narrows the acetabular angle (see above) (⊡ Fig. We hardly ever perform the Salter osteotomy ▬ Chiari osteotomy of the ilium, before the age of 2, preferring to wait and see how the ▬ triple osteotomies, situation develops spontaneously. Many mild cases of hip ▬ periacetabular osteotomies, dysplasia improve over time and do not require treatment ▬ shelf operations. Only if the acetabulum is very small, thus prevent- ing a stable closed reduction, do we follow the Salter All of these operations have their own indications and are osteotomy with an open reduction in the same session. Even in 2-year old patients we frequently await the spon- taneous outcome of events despite an acetabular angle of Salter’s osteotomy of the innominate bone (ilium): In over 30°, since the acetabulum can largely correct itself Salter’s osteotomy, the pelvis is divided above the during this stage of development provided the femoral anterior inferior iliac spine down to the transverse sci- head is well centered. Even more important than the acetabular angle for the evaluation is the shape of the lateral acetabular epiphysis and the concavity of the joint surface. If, by the age of 3 years, an acetabular angle of 30°, a flat epiphysis and inadequate concavity of the joint surface are all still present, then the Salter osteotomy is indicated. Since the operation is only feasible while the symphysis remains sufficiently mobile, it is no longer indicated after the age of 8. A Salter osteotomy can restore the normal hip configuration in small children and even excellent long- term results can be expected. Although one would expect lateralization of the femoral head to occur as a result of the angular movement with the center of rotation in the a b area of the epiphysis, this does not actually happen in reality. Principle of the Salter pelvic osteotomy (osteotomy of The postoperative management after a Salter oste- the innominate bone. The ilium is divided above the anterior inferior otomy involves fixation in a hip spica for 6 weeks. The iliac spine (a), the distal fragment is transposed ventrally/laterally, a triangular bone graft with the base facing laterally is wedged between fixation wires are subsequently removed and the child the fragments and fixed with a Kirschner wire (b) is mobilized. X-ray series for a 3-year old child with hip dysplasia (here fixed with an external fixator instead of an angled blade plate) involving an excessively steep acetabular roof and slightly off-center and a Salter pelvic osteotomy was performed on both sides with an hips on both sides (a). An intertrochanteric derotation varus osteotomy interval of 4 weeks (b). We The contralateral side should therefore be operated on at perform an acetabuloplasty most often for neuromuscular the earliest after 4–6 weeks. In principle, acetabulo- While the Salter osteotomy is a relatively simple and plasty is also a suitable operation for an excessively steep tried-and-tested operation, complications can still occur acetabulum in toddlers. A lesion of the sciatic nerve can oc- The correction options with acetabuloplasty are bet- 3 cur when the Gigli saw is used in the greater sciatic fora- ter than those with the Salter osteotomy, as the pivot men. We ourselves have had the misfortune to observe point with the former procedure is nearer the acetabulum an irreversible partial sciatic nerve lesion (after several (triradiate cartilage compared to the symphysis). Vascular injuries, delayed bone healing and ever, the risks associated with acetabuloplasty are greater. Furthermore, the osteotomy is performed closer to the joint and is technically more demanding Acetabuloplasty : An acetabuloplasty involves a dome- than Salter’s innominate osteotomy. The Various techniques have been described for the ace- tabuloplasty, the first originating from Koenig.

Situation 1 year postoperatively (d) At 14 years of age on completion of growth (b) pronounced trochan- 193 3 3 buy toradol 10 mg without a prescription pain treatment wellness center. The acetabulum is pulled ventrally and pressure in the joint is increased as a result of lengthening laterally purchase toradol 10mg visa pain treatment after knee replacement. A triangular wedge of bone secures the result- of the femoral neck, the procedure is indicated only if the ing position. The pivot point for the transfer is the sym- joint conditions are good (largely normal). This operation flattens an excessively steep ac- etabular roof, improves the roof coverage ventrally and Pelvic procedures narrows the acetabular angle (see above) (⊡ Fig. We hardly ever perform the Salter osteotomy ▬ Chiari osteotomy of the ilium, before the age of 2, preferring to wait and see how the ▬ triple osteotomies, situation develops spontaneously. Many mild cases of hip ▬ periacetabular osteotomies, dysplasia improve over time and do not require treatment ▬ shelf operations. Only if the acetabulum is very small, thus prevent- ing a stable closed reduction, do we follow the Salter All of these operations have their own indications and are osteotomy with an open reduction in the same session. Even in 2-year old patients we frequently await the spon- taneous outcome of events despite an acetabular angle of Salter’s osteotomy of the innominate bone (ilium): In over 30°, since the acetabulum can largely correct itself Salter’s osteotomy, the pelvis is divided above the during this stage of development provided the femoral anterior inferior iliac spine down to the transverse sci- head is well centered. Even more important than the acetabular angle for the evaluation is the shape of the lateral acetabular epiphysis and the concavity of the joint surface. If, by the age of 3 years, an acetabular angle of 30°, a flat epiphysis and inadequate concavity of the joint surface are all still present, then the Salter osteotomy is indicated. Since the operation is only feasible while the symphysis remains sufficiently mobile, it is no longer indicated after the age of 8. A Salter osteotomy can restore the normal hip configuration in small children and even excellent long- term results can be expected. Although one would expect lateralization of the femoral head to occur as a result of the angular movement with the center of rotation in the a b area of the epiphysis, this does not actually happen in reality. Principle of the Salter pelvic osteotomy (osteotomy of The postoperative management after a Salter oste- the innominate bone. The ilium is divided above the anterior inferior otomy involves fixation in a hip spica for 6 weeks. The iliac spine (a), the distal fragment is transposed ventrally/laterally, a triangular bone graft with the base facing laterally is wedged between fixation wires are subsequently removed and the child the fragments and fixed with a Kirschner wire (b) is mobilized. X-ray series for a 3-year old child with hip dysplasia (here fixed with an external fixator instead of an angled blade plate) involving an excessively steep acetabular roof and slightly off-center and a Salter pelvic osteotomy was performed on both sides with an hips on both sides (a). An intertrochanteric derotation varus osteotomy interval of 4 weeks (b). We The contralateral side should therefore be operated on at perform an acetabuloplasty most often for neuromuscular the earliest after 4–6 weeks. In principle, acetabulo- While the Salter osteotomy is a relatively simple and plasty is also a suitable operation for an excessively steep tried-and-tested operation, complications can still occur acetabulum in toddlers. A lesion of the sciatic nerve can oc- The correction options with acetabuloplasty are bet- 3 cur when the Gigli saw is used in the greater sciatic fora- ter than those with the Salter osteotomy, as the pivot men. We ourselves have had the misfortune to observe point with the former procedure is nearer the acetabulum an irreversible partial sciatic nerve lesion (after several (triradiate cartilage compared to the symphysis). Vascular injuries, delayed bone healing and ever, the risks associated with acetabuloplasty are greater. Furthermore, the osteotomy is performed closer to the joint and is technically more demanding Acetabuloplasty : An acetabuloplasty involves a dome- than Salter’s innominate osteotomy. The Various techniques have been described for the ace- tabuloplasty, the first originating from Koenig. Spitzy described a technique involving the insertion of a tibial bone graft, which then protruded laterally as in the shelf operation (see relevant section). Pemberton modified this technique and shifted the acetabulum not only distally, but anteriorly as well.
Glucagon is secreted by the pancreas and enhances the effects of cortisol on carbohydrate metabolism purchase toradol 10mg sciatica pain treatment exercise. After trauma purchase 10 mg toradol fast delivery phantom pain treatment, activity of insulin and similar anabolic proteins, such as insulin-like growth factor (IGF), is reduced. These anabolic proteins increase anabolic activity by increasing transcription of deoxyribonucleic acids, intracellu- lar translation, and decreased efflux and increased uptake of amino acids into the cell. They also act to increase lipolysis as an alternative substrate to protein catabolism. Attempts to reduce hypermetabolism beyond the clinical modalities previ- ously discussed have focused on the following: 1. Anabolic proteins such as growth hormone, insulin, and insulinlike growth factor 2. Glucocorticoid blockers (more recently) Growth hormone and insulinlike growth factor Growth hormone and insulinlike growth factor (IGF) levels are decreased follow- ing burn injury. Growth hormone and IGF-1 promote protein synthesis by increasing the cellular uptake of amino acids, accelerating nucleic acid transcrip- tion, and enhancing cellular proliferation. The anabolic protein growth hormone (GH), administered as rhGH, and the anabolic steroids oxandrolone [58,58a] and testosterone show promise in increasing lean body mass after burn injury. Catecholamine antagonists, such as propranolol and metoprolol, act to moderate the hypermetabolic effects of severe burn injury. In the acute setting, these anabolic properties can not only aid healing of the burn wound itself but also accelerate donor site healing. This allows for earlier recropping and ultimately earlier availability of autograft [60,61]. When hospital stay is adjusted to reflect percentage burn, hospital stay is reduced from 0. For a burn of 60%, this allows patient discharge 2 weeks earlier than is possible for patients with burns of similar size treated with placebo. Burned children, once released from the hospital, administered rhGH at a dosage of 0. Bone Bone mass is decreased following severe burn injury ( 40% TBSA) in adults and children. This is a result of reduced bone deposition and sustained hypercalci- uria. High levels of endogenous corticosteroid released in response to major burn- induced stress, immobilization, bone marrow suppression, aluminium toxicity from antacids and albumin, and magnesium deficiency are postulated as FIGURE 5 Changes in bone mineral content in major pediatric burns versus dis- charge from burn ICU. After severe burns, hypoparathyroidism also leads to addi- tional loss of bone mass. Long periods of immobilization lead to demineral- ization of bone, and bone marrow suppression results from sepsis and drug ther- apy. The consequences of bone loss are reduced peak bone mass, increased fracture risk, and loss of stature. Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) shows that both bone mass and bone mineral density are delayed by 2 years in burned children compared to unburned age- matched controls [68,69]. Labeled tetracycline techniques show evidence of de- creased bone formation, reduced surface area and osteoid area, and diminished reduced bone mineralization. TREATMENTS GROWTH HORMONE & MEDIATORS Burn injury greatly reduces endogenous levels of growth hormone and insulinlike growth factors such as IGF-1. When present in adequate quantities, protein synthesis is increased as a result of augmented cellular amino acid uptake, acceler- ated nucleic acid transcription and translation, and enhancement of cellular prolif- eration. Acute rhGH administration markedly reduces loss of essential and nonessential amino acids from muscle. Alanine efflux is attenuated, and efflux of glutamine and 3-methyl- histidine from muscle is abolished. In a double-blind placebo-controlled trial of growth hormone ad- ministration at 0. DEXA scanning demonstrated that this was attributable to significantly increased lean body (muscle) mass at 6, 9, and 12 months postburn.