Sominex
By H. Owen. Fitchburg State College. 2018.
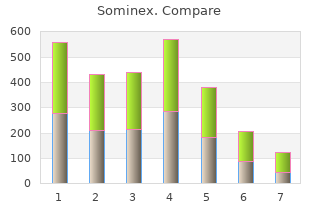
Decreased enzymatic activity order sominex 25 mg fast delivery insomnia 8 month old baby, including hepatic first-pass metabolism discount 25 mg sominex overnight delivery insomnia 9 weeks pregnant, is associated with the elderly, which may result in an increased oral bioavailabiliy for drugs subject to the first- pass effect. The effect of the shunt is to increase the presistence of the drug in the body and, provided the concentrations of the drug at its sites of action are sufficiently high, to prolong its duration of action. It is important to remember that although a drug molecule may be predominantly absorbed via one particular route/mechanism, it is also likely that suboptimal transport will occur via alternative routes and mechanisms. Diffusion is driven by a concentration gradient and is inversely related to molecular weight. The junctional complexes begin immediately below the luminal surface and are made up of three components (Section 1. Thus only small hydrophilic molecules, such as, for example, mannitol, are capable of squeezing through the junctional complexes to be absorbed via the paracellular route. The rate of absorption is governed by Fick’s Law and is determined by the physicochemical properties of the drug as well as the concentration gradient across the cells (Section 1. Carrier-mediated transport Amino acid transporters, oligopeptide transporters, glucose transporters, lactic acid transporters, monocarboxylic acid transporters, phosphate transporters, bile acid transporters and other transporters present on the apical membrane of the epithelial cells serve as carriers to facilitate nutrient absorption by the intestine. Drug moieties possessing similar structures to nutrients that are absorbed by such carriers may also be absorbed in this manner. Endocytic processes Considerable evidence has accumulated indicating that macromolecules and microparticulates can be taken up by the intestinal enterocytes, generally via pinocytosis. For example, studies have shown that receptor-mediated endocytosis via enterocytes is a major pathway for the intemalization of certain antisense oligonucleotides. In contrast, endocytic uptake of macromolecules and microparticles is carried out extensively by the M cells of the 144 Peyer’s patches. Transcellular shuttling through the M cells to the underlying Peyer’s patch may involve an adsorptive and/or receptor-mediated process, with membrane-bound vacuoles or vacuoles already present in the apical cytoplasm of the cells (see below, Section 6. Therefore, they are ionized to a certain extent, determined by their pKa and the pH of the biological fluid in which they are dissolved; the extent of ionization can be quantified by the Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation (see Section 1. According to the pH-partition hypothesis, the nonionized form of a drug, with a more favorable oil/water partition coefficient (Ko/w) than the ionized form, is preferentially absorbed. For example, the absorption of salicylic acid, a weakly acidic drug, is approximately twice as high at pH 4 than at pH 7. By contrast, quinine, a weakly basic drug, is absorbed approximately four times higher at pH 7 than at pH 4 (Table 6. The numbers refer to 1, atenolol; 2, practolol; 3, pindolol; 4, metoprolol; 5, oxprenolol; and 6, alprenolol. Generally, the larger the partition coefficient, the more lipophilic is a compound, and the more readily would it partition into biological membranes. By contrast, hydrophilic atenolol, with the smallest partition coefficient, shows the lowest permeability. Some drugs exhibit a lower absorption than expected on the basis of their partition coefficient. This reduced absorption is thought, in some cases, to be due to the P-glycoprotein efflux effect (see above, Section 6. The results shown with the squares represent the relationship between intestinal absorption clearance (ka) observed from the in situ jejunum loop in the presence (■) and absence (□) of cyclosporin A in rats and octanol-buffer (pH 7. The numbers refer to 1, atenolol; 2, nadolol; 3, acetamide; 4, celiprolol; 5, acebutolol; 6, doxorubicin; 7, timolol; 8, sulfathiazole; 9, quinidine; 10, sulfamethoxazole; 11, digoxin; 12, cyclosporin A; 13, vinblastine; 14, b-estradiol; 15, verapamil. The ionized form of a drug displays a higher dissolution rate and greater solubility than the nonionized form (see Section 1. Drug solubility is also a function of the crystalline, hydrate and salt form (see Section 1. For example, the amorphous form of a drug moiety is usually more soluble than the corresponding crystalline form (e. The solubility of a salt form of a lipophilic drug is higher than the free form and conversion of the free base to the corresponding salt represents a common method of increasing drug solubility. Symposium on Drug Absorption, Metabolism and Excretion, Scientific section of the American Pharmaceutical Asso. The Noyes-Whitney equation describes the influence of surface area (S) and other factors on the dissolution rate: (Equation 6. A reduction in particle size results in an increase in the surface area, which facilitates an increase in the dissolution rate and therefore, also, an increase in the rate of absorption. Drugs administered as suspension are generally rapidly absorbed because of the large available surface area of the dispersed solid.
White blood cells that are decreased in number or abnormal in appearance may indicate Immunology/Apply knowledge of fundamental further testing sominex 25mg overnight delivery sleep aid med. Which test should be performed when a patient IgA-deficient person who has formed anti-IgA has a reaction to transfused plasma products? Red cell enzymes IgA is usually absent from secretions generic 25 mg sominex mastercard insomnia locations, but the B-cell Immunology/Evaluate laboratory and clinical data to count is usually normal. What is the “M” component in monoclonal or cell line produced in a monoclonal gammopathy gammopathies? Monoclonal antibody or cell line Immunology/Apply knowledge of fundamental biological characteristics/Immunoglobulins/Testing/1 106 3. A child suspected of having an inherited humoral Answers to Questions 5–9 immunodeficiency disease is given diphtheria/ tetanus vaccine. B In an immunodeficient patient, the expected his level of antibody to the specific antigens is levels of specific antibody to the antigens in the measured. Which result is expected for this patient vaccine would be decreased or not present. An increase in IgG-specific antibody but not of plasmacytoid lymphocytes involving both the IgM-specific antibody bone marrow and lymph nodes. Increased levels of nonspecific antibody secrete monoclonal IgM and are in transition from B Immunology/Evaluate laboratory data/ cells to plasma cells. In contrast to multiple myeloma, Immunoglobulins/Testing/2 osteolytic bone lesions are not found. D DiGeorge’s syndrome is caused by a developmental spike on an electrophoretic pattern? Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome cytometry is most helpful in determining numbers Immunology/Evaluate laboratory data to make and subpopulations of T cells. In testing for DiGeorge’s syndrome, what type antisera indicate excessive light-chain excretion. C Serum-free light chains are a sensitive indicator identifications/T cells/Testing/2 of a monoclonal gammopathy. Increased polyclonal Fab fragments to quantitate immunoglobulin heavy- or light-chain D. Immunology/Evaluate laboratory data to make identifications/Immunoglobulins/Testing/2 9. Free monoclonal light chains are often present in the serum of multiple myeloma patients, and may be useful for disease monitoring. Which of the following assays would be recommended to detect the presence of serum-free light chains? Immunology/Apply principles of basic laboratory procedures/Complement/Testing/1 11. Immunodeficiency disorders such as common The inflammatory response seen in malignancy variable immunodeficiency and acute infections gives rise to an increase in C. Bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic infections caused by an inherited deficiency in complement Immunology/Evaluate laboratory data to make constitutes only about 1% of immunodeficiency identifications/Complement/Testing/2 diseases. All of the following tests measure phagocyte a deficient serum level of only one complement function except: factor. Di Hydro rhodamine reduction assay tests are used to diagnose chronic granulomatous C. It causes B-cell proliferation and increased production of antibody, interferon, and other cytokines. A patient had surgery for colorectal cancer, after Answers to Questions 1–3 which he received chemotherapy for 6 months. No useful clinical information in this case that is elevated in 70%–80% of patients with ovarian Immunology/Apply principles of basic laboratory cancer and about 20% of patients with pancreatic procedures/Tumors/Testing/1 cancer. Which of the following substances, sometimes cancer; and the fast-migrating liver isoenzyme, which used as a tumor marker, is increased two- or is a marker for metastatic liver cancer. Neuron-specific enolase is an Immunology/Tumor markers/Testing/1 enzyme that is used as a tumor marker primarily for 6. High levels may be digital-rectal examination caused by prostate malignancy, benign prostatic B. The sensitivity is sufficiently high to with malignant disease warrant its use as a screening test, but sensitivity for Immunology/Correlate laboratory data with stage A cancer is below 60%.